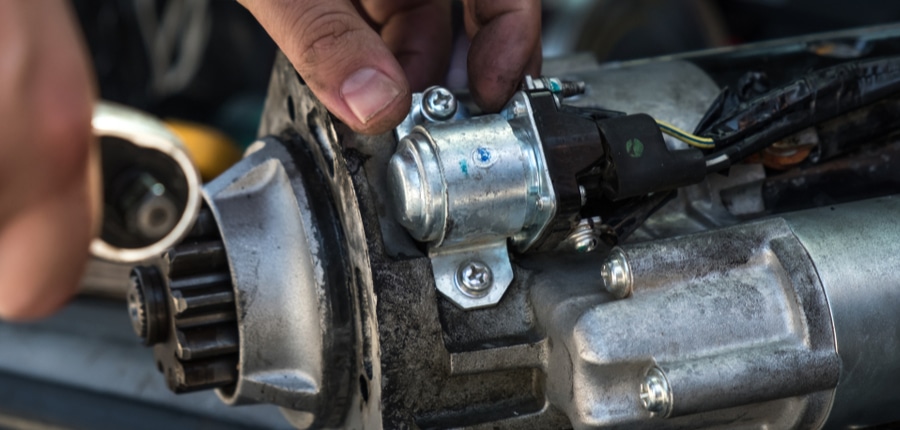
A starter is essentially a strong electric motor that cranks the engine of a vehicle, allowing it to begin its fuel-powered operation. It draws a great deal of current from the battery to turn the engine.
As with any high-current electrical device, reliable switching of power is difficult. Starter motors almost always have an integrated solenoid that switches current into the motor. This solenoid also advances the starter gear to engage the teeth of the flywheel between the engine and the transmission.
Most starters are reasonably accessible on the side of the engine and not too difficult to replace, with the vehicle on a lift. Sometimes they are obstructed by the exhaust system, heat shields, transmission brackets, or engine mounts, but most of the time replacement is fairly straightforward.
Costs of Starter Replacement
In most cases, a starter replacement begins with a standard starting/charging system diagnosis. Some shops will do parts of this for free, but a comprehensive test is more commonly done for either a flat fee of $30 to $50 or sometimes at a labor charge of half an hour.
Below are some estimates for the cost to replace a starter on some common vehicles using a labor rate of $150 an hour:
- 2011 Chrysler 200, 2.4-liter engine – the labor time for starter replacement is 1.2 hours. A remanufactured Mopar starter lists for $208, and a new TYC replacement is about $110. The total job cost would be about $388 using factory parts and around $290 when using aftermarket parts.
- 2009 Ford Escape, four-wheel-drive, 3-liter engine—this will take about 0.8 of an hour of labor time to replace the starter. A remanufactured Motocraft part lists for $241, and a new ACDelco starter costs about $170. The total estimated cost for the job is about $361 using factory parts or about $290 with aftermarket parts.
- 2000 Volkswagen Beetle, automatic transmission, 1.8-liter turbocharged engine—the labor time for the starter replacement of this particular vehicle is 2.1 hours. A new OE starter lists for $556, and a new Bosch starter costs around $270. The total estimated cost for the job is about $871 using factory parts or about $585 with aftermarket parts.
- 2007 Toyota Tacoma, four-wheel-drive, 4-liter engine—labor time for starter replacement of this vehicle is around 1.2 hours. A new OE starter lists for $217, and a new Remy starter is around $210. This makes the starter replacement cost around $397 when using factory parts and about $390 when using aftermarket parts.
Of course, several factors would affect the total cost of replacing the starter. For one, labor rates can differ significantly depending on the auto shop you visit and its location.
Also, as there can be a plethora of suppliers of auto parts, prices can vary greatly depending on the state they are in. It is even possible that the same OE parts prices can vary depending on the markup over cost in a particular location.

New Versus Remanufactured Parts
The above estimates are for new parts (except where new OE parts are discontinued). However, it is usually possible to find remanufactured starters as well, and the prices are typically lower.
Starters are relatively simple electrically and easy to remanufacture, as most of the internal parts aren’t subject to harmful wear. But, as with most things, the reliability of new parts is usually better.
One thing to keep in mind is a warranty, as there are a wide variety of different warranty policies between brands and new vs. remanufactured. While some remanufactured starters come with a lifetime warranty, some new starters have only a 12-month warranty; it’s always best to check the warranty terms and factor those in along with the price.
Diagnosing a Starter with a Multimeter
This is one thing most people could do at home, and a multimeter is a good tool to have for a large number of different things that come up in a household.
First, as with any automotive electrical diagnosis, you want to make sure that the battery is good and fully charged. You can do that by checking the voltage of the battery; with everything off, it should be sitting at 12.6 volts. If it’s at 12.4 or less, charge the battery. If you don’t have a charger, then most auto parts stores can charge and test batteries.
Once the battery is fully charged and everything is all together, look at the voltage of the battery as you turn the key on. You should see the voltage drop by maybe a tenth of a volt. Then try to start the vehicle. Under ordinary circumstances, that would engage the starter motor and draw a great deal of current, and you’d see the battery voltage drop to about 10.5 volts while cranking. If it does that but all you hear is a click (the starter solenoid energizing), it’s probably a bad starter. If it drops lower, it’s probably a bad battery. If you hear a click and it only drops to about 12.3 volts, that’s probably a bad starter solenoid. If you don’t hear a click and the voltage doesn’t drop, then it might not be a starter problem.
What Else Could it Be?
This is a fairly important question. Once in the 90s, this writer worked as an electrical parts rebuilder, and starters were particularly easy, as about 50% of the ones we got were just fine. We’d still freshen up the worn parts, but very often they’d been replaced for no good reason. It’s understandable that if a vehicle won’t crank over, people are often willing to throw money at the problem, but there are many other things that can cause that.
A starter needs a great deal of current to operate; when one begins to fail, the most common thing to suspect is the battery that provides that current or the cable connections that transfer the current. The battery and the battery connections should be checked and either ruled out or addressed before going further. Corrosion on the battery terminals is one of the main things to look for.
Related cost articles: Battery Replacement and Battery Cable Replacement
Sometimes there is also a relay that triggers the starter solenoid, which is usually checked easily by swapping it out for a known-good relay. Most vehicles that use a starter relay also use an identical relay for the AC clutch, and those two can be swapped.
If there is no “click” noise and no measurable current being drawn from the battery when the key is turned over to start, the problem might be the ignition switch itself, or something related to the PCM or the anti-theft system. Most vehicles nowadays have security systems that monitor various conditions and prevent the starter from actuating until all the necessary parameters are met. In many cases, a damaged keyfob won’t start the vehicle, and some vehicles won’t start if the battery in the keyfob is low.
Another possible cause of a no-crank condition is the neutral safety switch if the vehicle has a manual transmission or the transmission range sensor on an automatic. Both are designed to disable the starter solenoid if the transmission conditions aren’t correct. On an automatic, you can sometimes test that by shifting to neutral and seeing if it will start then.
The starter drive gear engages the gear teeth of a flexplate (or flywheel, if a manual transmission) that sits between the engine and transmission. There is a drive gear on the starter motor that meshes with the flywheel. Sometimes, the starter drive gears fail, and sometimes they damage the teeth of the flywheel. This is usually easy to tell, as a failure makes a lot of noise when trying to start.
FAQ’s
- What is the most common reason a starter won’t crank the engine?
The battery being discharged is the most common cause. That can be from a battery problem, from something having been left on, or even from a vehicle not being driven on long trips often enough. The second most common problem is a bad cable connection at the battery.
- Can I replace my own starter?
There are some engines where the starter is accessible without the vehicle being on a lift, but usually it’s a somewhat difficult job requiring some effort to gain access.
- Where is the best place to diagnose a starting problem?
That depends on what the problem winds up being, which you don’t know in advance. If it’s a conventional starter, battery, or connection issue, an auto-electric shop would be the best. If it’s a problem with the security system, a dealership or well-equipped independent shop would be the best way to go.
